What is Pes Plano Valgus? Learn more about this condition
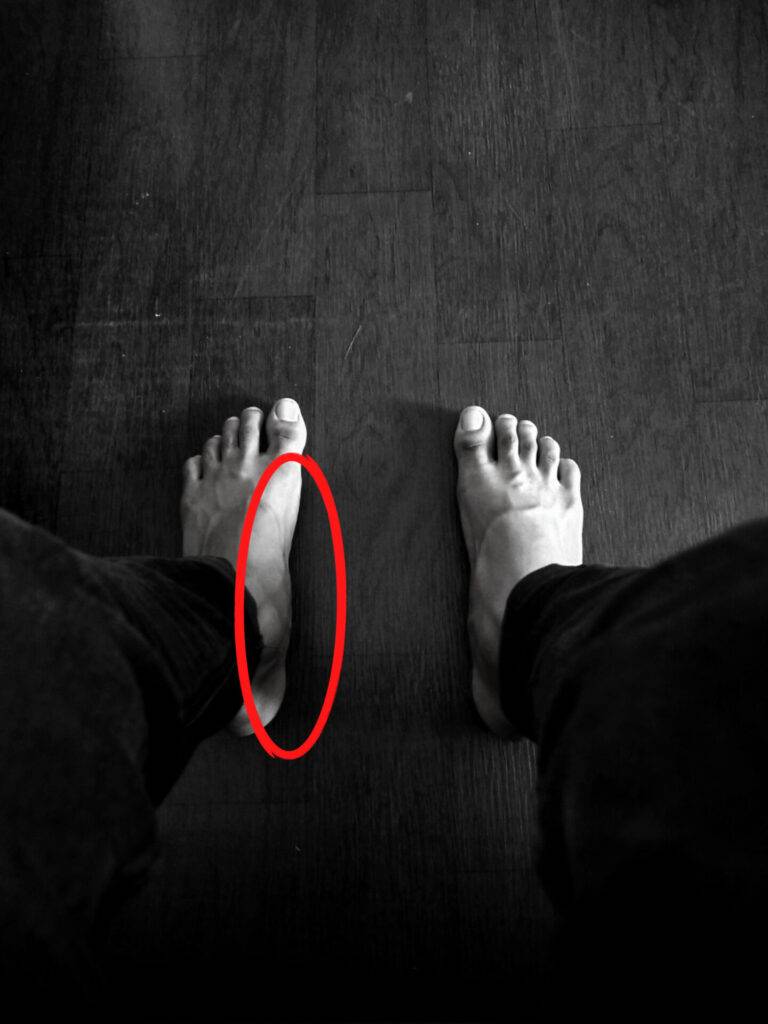
Pes plano valgus is the medical term that refers to an abnormal foot due to a flattened arch, a rolled-in appearance of the ankle, and a heel that appears to be rolled-out from under the ankle. It is usually flexible, meaning that the joints of the foot and ankle are mobile.
When sitting, a person with pes plano valgus may have a reasonably well-formed arch. However, when the person stands, the arch flattens, the ankle rolls in, and the heel rolls out (everts). This complex set of position changes between sitting and standing is called pronation of the foot. A pes plano valgus foot is often maximally pronated.
What Causes Pes Plano Valgus/Flat Feet?
This condition can be congenital (e.g., birth) or acquired (e.g. adults, increased exposure to weight-bearing).
- Congenital flat feet occur when someone is born with or predisposed to having a more flexible midfoot region resulting in pronation or collapsing of the arch. Ethnicity is a crucial factor surrounding flat feet, with the condition being more likely in certain indigenous cultures.
- Acquired flat feet causes include a loss of active (e.g. intrinsic foot and ankle stabilisers) or passive support (ligamentous laxity, hypermobile joints). The lack of support during vigorous weight-bearing activities exaggerates the flatness. Muscular weakness in the ankle and arch stabilisers is the most common etiological factor for flat feet. Research suggests the tibialis posterior muscle is the most integral in stabilising the medial longitudinal arch via its insertion into the arch’s bony roof. When your arch stabilisers like this perform sub-optimally, the arch slowly pronates and flattens towards the ground when weight and force apply down through the foot.
Symptoms of Pes Plano Valgus/Fallen Arches
- pain in the forefoot with walking
- difficulty getting shoes to fit
- increased discomfort from shoes that were previously comfortable
- tenderness to touch on the bases of the toes (metatarsals)
- flattening of the plantar surface of the foot
Moreover, flat feet slowly progress as you increase your feet’s exposure to weight-bearing activities. The two most common progressions from flat feet are foot deformities and bony stress injuries. Hence, without an appropriate rehabilitation program and continuing active or passive instability, structures surrounding or supporting the arch can load inappropriately and unsafely to cause compounding problems.
Are you suffering from this condition? One of our podiatrist can assist and help what treatment options are best for you. ✅
Schedule an appointment here or you may call us at 44 (0) 207 101 4000. 📞
We hope you have a feetastic day! 👣☀️
-The Chelsea Clinic and Team